
ANALYSIS OF THE INFLUENCE OF KEY PARAMETERS AND DRIVING MODES OF FLUID COUPLINGS ON THEIR OPERATING CHARACTERISTICS
2025-12-11 13:49How does the density of the working fluid in a hydrodynamic coupling affect its characteristics?
The torque transmission capacity of a hydrodynamic coupling is directly proportional to the first power of the working fluid density; therefore, the higher the working fluid density, the greater the transmitted torque. For example, a hydrodynamic coupling using water as the working medium has a torque transmission capacity 1.15 times that of a hydraulic coupling using oil as the working medium.
How does the viscosity of the working fluid in a hydrodynamic coupling affect its characteristics?
Higher working fluid viscosity increases friction on the impeller's working chamber, resulting in greater flow resistance and a lower circulating speed, thus reducing the transmitted torque. Lower working fluid viscosity provides better fluidity and a greater torque transmission capacity, but excessively low viscosity is detrimental to lubrication and sealing.
How does the temperature of the working fluid in a hydrodynamic coupling affect its characteristics?
Higher working fluid temperature results in lower viscosity, better fluidity, reduced friction on the working chamber surface, lower power loss, and increased transmitted torque. However, excessively high temperatures can cause the working fluid to age, the machinery to deform, and the seals to fail. Therefore, the working fluid temperature is usually controlled at (65±5)℃, with a maximum of 90℃.
What is the effect of the fluid filling rate on the characteristics of a fluid coupling?
(1) It affects the transmitted power. More fluid results in greater transmitted power; conversely, a lower filling rate leads to lower transmitted power.
(2) It affects slip and output speed. With a constant external load, a higher filling rate results in a lower slip and higher output speed; conversely, a lower filling rate results in a higher slip, lower output speed, and increased heat generation.
(3) It affects the stability of the coupling. A low filling rate increases the coupling's unstable region; a high filling rate reduces the coupling's unstable region.
What are the different driving methods for fluid couplings, and how do they affect their characteristics?
Hydraulic couplings have two driving methods: internal wheel drive and external wheel drive, as shown in Figure. 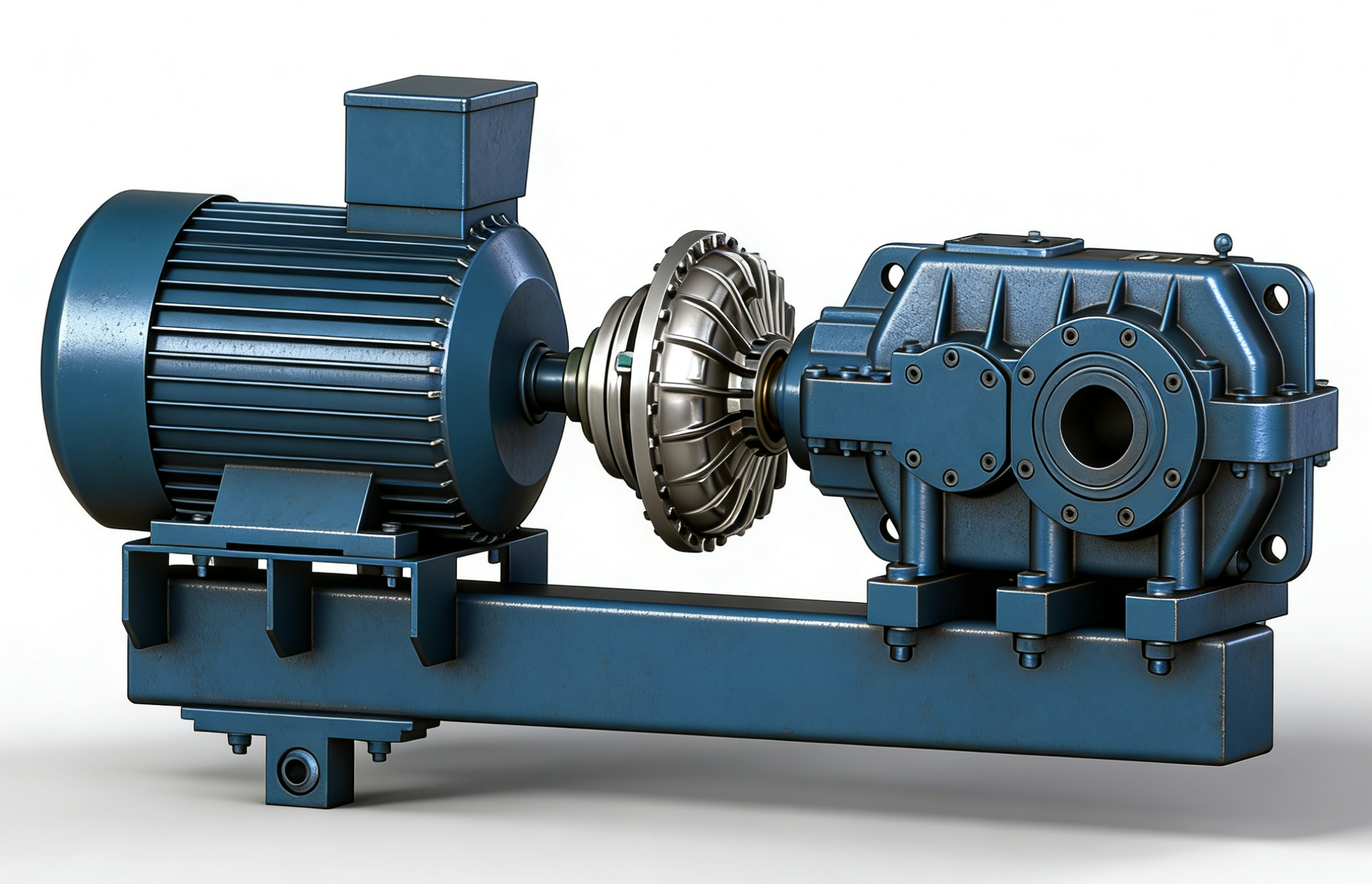 (a) Internal wheel drive;
(a) Internal wheel drive;
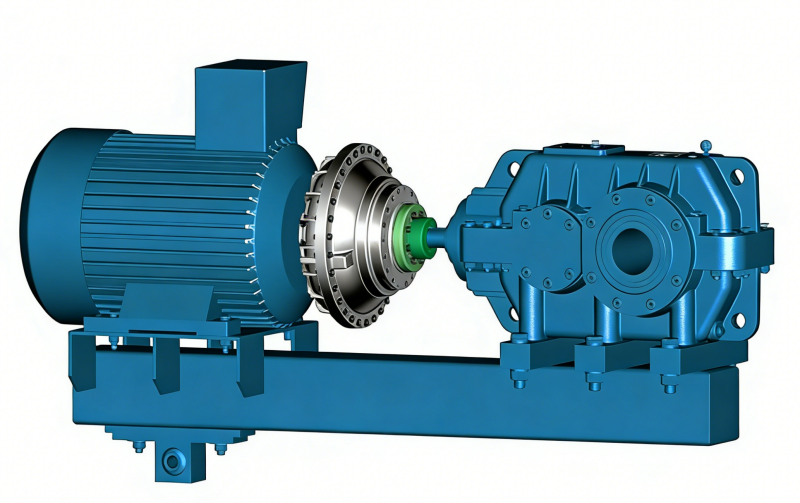 (b) External wheel drive
(b) External wheel drive
(1) Internal wheel drive: The impeller inside the chamber acts as the pump wheel, and the external impeller acts as the turbine. The mass of the coupling is borne by the motor shaft (the coupling is at the reducer end).
(2) External wheel drive: The impeller inside the chamber acts as the turbine, and the external impeller acts as the pump wheel. The mass of the coupling is borne by the reducer (the coupling is at the motor end).
(3) Specially designed internal wheel drive hydrodynamic couplings have characteristics that are not significantly different from external wheel drive couplings.
(4) Reversing the input and output of an original external wheel drive coupling will change its characteristics to some extent, but generally does not affect its use.
